++ 50 ++ 5 h's of pheochromocytoma 454354-5 h's of pheochromocytoma
What are the 5 H's of pheochromocytoma? · INTRODUCTION Pheochromocytoma is a rare neuroendocrine tumor, occurring in less than 02 percent of patients with hypertension In approximately 60 percent of patients, the tumor is discovered incidentally during computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the abdomen for unrelated symptoms The treatment of pheochromocytoma will bePALLOR or FLUSHING of the face, NAUSEA and VOMITING, pain in the CHEST and ABDOMEN, and paresthesias of the extremities The incidence of malignancy is as low as 5% but the pathologic distinction between benign and malignant pheochromocytomas is not

Pheochromocytoma Risk Factors Causes And Symptoms
5 h's of pheochromocytoma
5 h's of pheochromocytoma- · Chen H, Sippel RS, O'Dorisio MS, Vinik AI, Lloyd RV, Pacak K (10) The NANETS Consensus guidelines for the diagnosis and management of neuroendocrine tumors pheochromocytoma, paraganglioma, and medullary thyroid cancer Pancreas 39(6)775–7 PubMed PubMedCentral CrossRef Google ScholarA pheochromocytoma (PCC) is a rare tumor that usually grows in your adrenal glands, above your kidneys It's also known as an adrenal paraganglioma or a




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
Ninety percent of patients are cured by surgery to remove benign pheochromocytoma tumors 3 Surgery for tumor removal is typically done by laparoscopy, during which a small incision is made in the abdomen 3,4 During surgery to remove the tumor, the physician will usually examine nearby organs to determine whether the pheochromocytoma has spread to other parts of the bodyThe search for pheochromocytoma consisted of clinical evaluation, 24 h determination of urinary catecholamines and adrenal imaging The mean age at genetic diagnosis of MEN 2 was 140/70 years, the mean duration for the followup was 76/28 yearsPheochromocytoma are found in 2 out of every million people each year and are the cause of high blood pressure in less than 02% of people with high blood pressure However, because pheochromocytoma release adrenaline in uncontrolled bursts, they can cause serious health problems like stroke, heart attacks, and even death
· If you have a pheochromocytoma, the tumor releases hormones that may cause high blood pressure, headache, sweating and symptoms of a panic attack If a pheochromocytoma isn't treated, severe or lifethreatening damage to other body systems can result Most pheochromocytomas are discovered in people between the ages of and 50 · The excision of a pheochromocytoma is a variant of an adrenalectomy, which is the removal of one or both adrenal glandsWhen the tumor being removed is a pheochromocytoma, careful preoperative optimization and intraoperative management are required to ensure hemodynamic stability during the procedure Surgical resection can be performed via open · About 5 h after the first 2 mg highdose DST, the patient suddenly developed nausea and vomiting, headache, and restlessness in concert with hypertension (BP 2/1 mmHg), chest pressure, and tachycardia An electrocardiogram (ECG) revealed tachycardia and
Headache, sweating, and a fast heartbeat are typical symptoms, usually in association with markedly high blood pressureA pheochromocytoma secretes catecholamine hormones (adrenaline and related hormones) that are responsible for the/03/02 · Followup information confirming lack of pheochromocytoma was obtained in 330 of the 546 patients in whom imaging studies were used to exclude pheochromocytoma (mean followup, 25 years;Pheochromocytoma produce an excess amount of catecholamine hormone, which include norepinephrine (noradrenaline), epinephrine (adrenaline), and dopamine The release of catecholamines can cause persistent or episodic high blood pressure, headache, sweating and other symptoms



2




Pheochromocytoma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org
The biggest problem for pheochromocytoma is to suspect it in the first place Elevated metanephrines establish the diagnosis With the proper preoperative preparation the risks during operation and the postoperative period are minimal If there is aThe symptoms and signs of a phaeochromocytoma can include headaches heavy sweating a rapid heartbeat (tachycardia) high blood pressure a pale face feeling or being sick feeling anxious or panicky shakiness (tremor)Hypertension, Headache, Hyperhydrosis, Hypermetabolism, Hyperglycemia What urine test is performed to diagnose pheochromocytoma?



Cellular Uptake Of A Fluorescein Labeled Ab40 F Ab40 And Alexa Fluorh Download Scientific Diagram



Mysterious Inhibitory Cell Regulator Investigated And Found Likely To Be Secretogranin Ii Related Peerj
· (See "Pheochromocytoma in genetic disorders" and "Treatment of pheochromocytoma in adults" and "Paragangliomas Epidemiology, clinical presentation, diagnosis, and histology") EPIDEMIOLOGY Catecholaminesecreting tumors are rare neoplasms, probably occurring in less than 02 percent of patients with hypertension 1,2 · Patients with signs or symptoms of pheochromocytoma;Pheochromocytoma may present in a ' classic ' manner or as an explosive, lifethreatening cardiov ascular, neurological or meta bolic crisis The classic triad of headache, diaphoresis and




Pheochromocytoma




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
Although recurrent pheochromocytoma disease is rare, approximately 50% of patients with recurrent pheochromocytoma disease will experience distant metastasis The 5year survival in the setting of metastatic pheochromocytoma cancer (whether identified at the time of initial diagnosis or identified postoperatively as recurrent disease) is 40% to 45% · Pheochromocytoma in 5 7% Also café au lait spots, iris hamartomas, axillary or inguinal freckling, osseous dysplasia and optic pathway glioma (Cancer Genet 12;51) Familial paraganglioma inactivating mutations in succinate dehydrogenase tumor suppressor gene Associated with pheochromocytoma in 3 5% · J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 12;




Pheochromocytoma




Medical Mnemonics Pptx Powerpoint
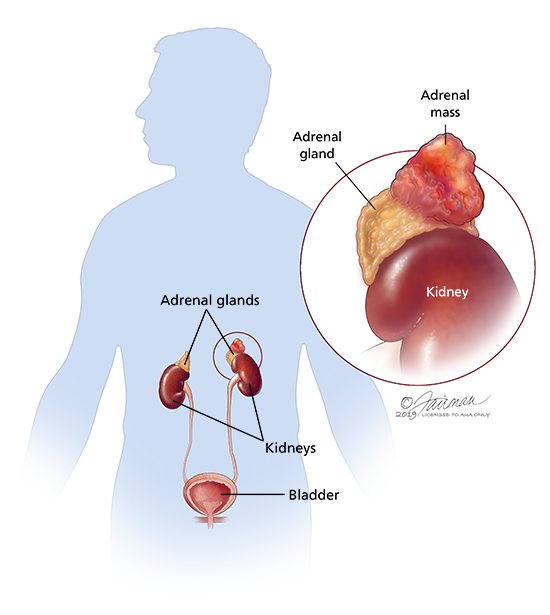
· Pheochromocytoma is a relatively rare tumor of the adrenal glands or of similarly specialized cells outside of the adrenal glands; · Biochemical evaluation for pheochromocytoma revealed elevated urine norepinephrine (NE) of 738 μg/24 h (with an upper reference limit of 100 μg/24 h) and epinephrine (EPI) of 779 μg/24 h (upper reference limit, 24 μg/24 h) Two days later, the patient underwent hernia repair with blood pressure and heart rate controlled by iv α and βPheochromocytoma is a type of neuroendocrine tumor that grows from cells called chromaffin cells These cells produce hormones needed for the body and are found in the adrenal glands The adrenal glands are small organs located in the upper region of the abdomen on top of the kidneys About 8085% of pheochromocytomas grow in the inner layer of




Pheochromocytoma Amboss



1
–315 ©12 Wiley Periodicals, Inc To address the unique challenges in the diagnosis and management of small pheochromocytomas, the authors performed a retrospective study of 24 patients with small pheochromocytomas (≤3 cm) treated between 1995 and 11, using 51 patients with larger pheochromocytomas (>3 cm) as · Pheochromocytoma (PH) and paraganglioma (PG) are neuroendocrine neoplasms arising from chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla and the sympathetic ganglia, respectively Although are unusual cause of hypertension (HT) accounting for at most 01–02 % of cases, they may lead to severe and potentially lethal hypertensive crisis due to the effects of the releasedPheochromocytoma is typically associated with a symptom triad of headache, palpitations, and diaphoresis Hypertension, either sustained or paroxysmal, is the clinical hallmark of pheochromocytoma and is commonly attributed to catecholamine excess The classic triad, combined with hypertension, suggests the diagnosis of pheochromocytoma with 93




Em Hyperkalemia And Endocrine Emergencies Flashcards Quizlet




Addision Cushing Nursing Studocu
Jacobson AF, Deng H, Lombard J, et al 123Imetaiodobenzylguanidine scintigraphy for the detection of neuroblastoma and pheochromocytoma results of a metaanalysisThe classical symptom triad consists of episodic palpitations, headaches and sweating Pallor, nausea and panic attacks are other reasonably common symptoms although they may present very nonspecifically 3 – 8% of all adrenal incidentalomas are thought to be undiagnosed phaeochromocytomas3,4 · Pheochromocytoma, or "pheo," is a rare tumor that develops in the adrenal glands It affects the production of adrenalin and can result in high blood pressure and other health concerns



Jim Bmj Com Content Jim 65 2 396 Full Pdf




Pheochromocytoma Symptoms Treatment Diagnosis Prognosis
· Blood Testing, Urine Testing, and Laboratory Testing for Pheochromocytoma Diagnosis There are very specific blood and urine tests that are requried to test for and diagnose pheochromocytoma Since pheo's secrete adrenaline and other adrenalinerelated compounds, the bood and urine tests are aimed at measuring these hormones and their breakdown products24 hour collection of urine to detect metanephrine, · Scans for pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma is discussed here IMPORTANT If you have a pheochromocytoma or paraganglioma you need (in, preparation for curative surgery) to be treated with medications until your pheochromocytomas or paraganglioma is removed The goal is to obtain stabilization in the blood pressure for 12 weeks prior to surgery




Pheochromocytoma Risk Factors Causes And Symptoms




Applications Of Nmr Spectroscopy To Systems Biochemistry Abstract Europe Pmc
· Pheochromocytoma causes a variety of signs and symptoms, including (in alphabetical order) Pheochromocytoma causes a variety of signs and symptoms, including (in alphabetical order) Skip to main content US Department of Health and Human Services National Institutes of Health Directory Follow follow us on Facebook follow · Pheochromocytoma is a rare tumor of the adrenal gland It often presents with the classic triad of headache, palpitations and generalized sweating Although not described as a typical symptom of pheochromocytoma, anxiety is the fourth most common symptom reported by patients suffering of pheochromocytomaA pheochromocytoma is a tumor that usually originates from the adrenal glands' chromaffin cells, causing overproduction of catecholamines, powerful hormones that induce high blood pressure and other symptoms High blood pressure is the most important symptom, but a fast and pounding pulse, excessive sweating, lightheadedness when standing




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders
Pheochromocytoma is a rare type of tumor that arises from certain cells known as chromaffin cells, which produce hormones necessary for the body to function properly Most pheochromocytomas originate in one of the two adrenal glands located above the kidneys in the back of the upper abdomen · Pheochromocytoma (PCC) is a rare kind of tumor that forms in the middle of the adrenal glands The tumors cause your adrenal glands to make too many hormones · Pheochromocytoma can occur at any age However, it is diagnosed most frequently between the ages of 30 and 501 Up to % of pheochromocytomas are diagnosed in children2




Pheochromocytoma Wikipedia




Em Hyperkalemia And Endocrine Emergencies Flashcards Quizlet
Intrapancreatic pheochromocytoma There were 3 intraadrenal and 1 intraabdominal pheochromocytomas The majority of all tumors were located within 1 of the adrenal glands in 5 cases they were bilateral The average weight of 81 AFIP and 16 MMH pheochromocytomas was 90 gm The smallest tumor nodule weighed 19Phaeochromocytomas are rare neuroendocrine tumours with a highly variable clinical presentation but most commonly presenting with episodes of headaches, sweating, palpitations, and hypertension The serious and potentially lethal cardiovascular complications of these tumours are due to the potent effects of secreted catecholamines Biochemical testing forSWEATING, palpitation, apprehension, TREMOR;




Pheochromocytoma Presentation Epinephrine Endocrine System



Genitourinary System
Range, 178 years) Only 1 case of pheochromocytoma was confirmed by followup in a patient with a previously negative computed tomographic scan resultDiagnosing Pheochromocytomas The diagnosis of pheochromocytoma hinges on the treating physician entertaining the diagnosis in the first place Making the diagnosis is usually straightforward by performing the following tests 24hour urinary catacholamines and metanephrinesThe signs and symptoms of a pheochromocytoma are those related to sympathetic nervous system hyperactivity The classic triad includes headaches (likely related to elevated blood pressure, or hypertension), tachycardia /elevated heart rate, and diaphoresis (excessive sweating, particularly at night, also known as hyperhidrosis)




Pheochromocytoma Radiology Reference Article Radiopaedia Org




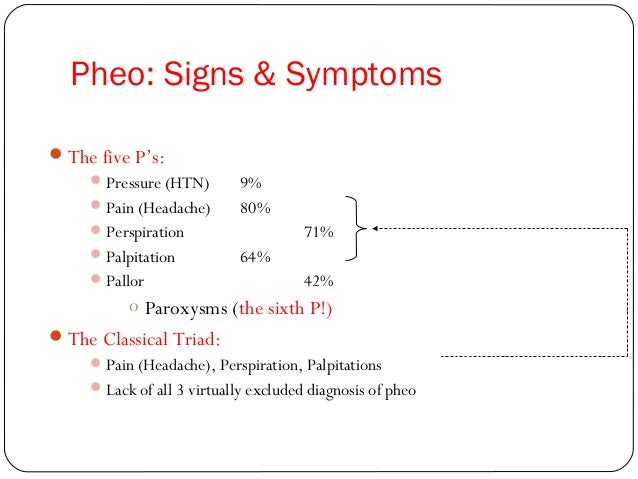
Edgar V Lerma Pheochromocytoma 5 Hs H Ypertension H Eadache H Yperhidrosis H Yperglycemia H Ypermetabolism Nephpearls Asnbrcu T Co Xcgcbcytr8
· Pheochromocytoma – 5 Ps December 23, 09 Signs and symptoms of pheochromocytoma – 5 Ps palpitations, pallor, perspiration, pain, pressure (increased) Related Posts More on pheochromocytoma Leave a Reply Cancel reply Your email address will not be published Required fields are marked * Comment Name * Email *Phaeochromocytoma (pheochromocytoma in American spelling) is a rare neuroendocrine tumour that secretes high amounts of the catecholamines noradrenaline and, to a lesser extent, adrenaline Phaeochromocytomas arise from the adrenal medulla (85%) or from neural ganglia in the head and neck (15%) The latter are also termed paragangliomas · A tumour arising from catecholamineproducing chromaffin cells of the adrenal medulla that classically presents with headaches, diaphoresis, and palpitations in the setting of paroxysmal hypertension Neumann HPH, Young WF Jr, Eng C Pheochromocytoma



Immunogenic Neoantigens Derived From Gene Fusions Stimulate T Cell Responses Nature Medicine




Hyoldq S And Nuemonics Autosaved By Willliams Issuu
· During severe attacks, there may be HEADACHE;




Jefferson Alumni Bulletin Volume Xii Number 5 December Pdf Free Download



2




Pdf Surgery Without Blood Transfusion For Giant Paraganglioma In A Jehovah S Witness Patient




Binla Book




History Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertension Ppt Video Online Download




Pheochromocytoma Symptoms Diagnosis And Treatment




Endocrine Hypertension Sciencedirect



Http Www Ucsfcme Com 17 Mdm17p01 Slides 3 Final schedule one time print Mdm17p01 Pdf



Pheochromocytoma By Kate Hammett



Pheochromocytoma Adrenal Medulla Tumor Symptoms Diagnosis Treatment Urology Care Foundation




Pheochromocytoma Amboss




Jaypeedigital Ebook Reader



Tsukuba Repo Nii Ac Jp Action Repository Action Common Download Item Id Item No 1 Attribute Id 17 File No 1




Pathology Mnemonics Key Notes



2



Www Iridiamedical Com Docs Emergency Manual 6 17 13 Pdf



Pheochromocytoma And Its Anaesthetic Management
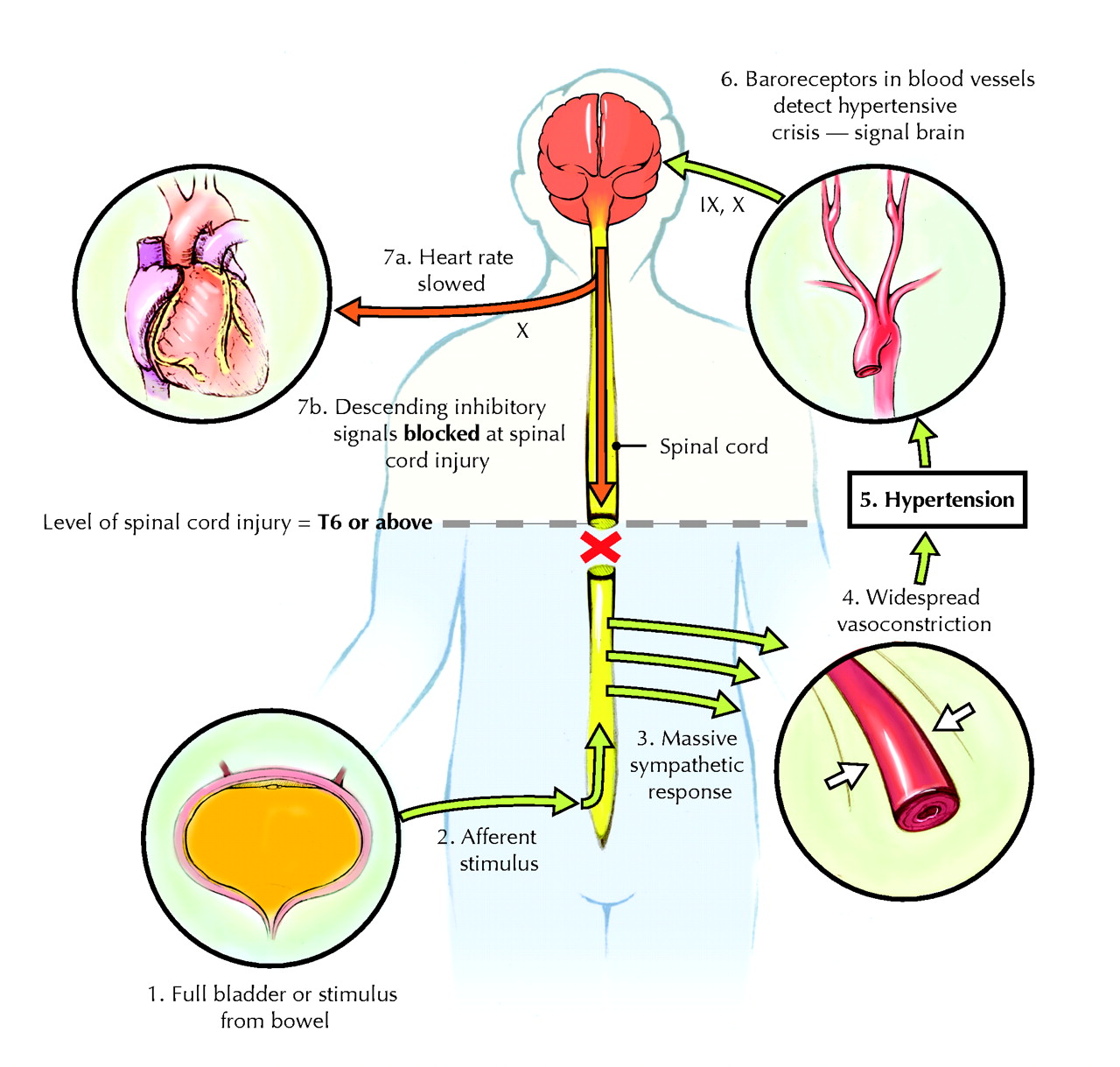



Rehabilitation Medicine 1 Autonomic Dysreflexia Cmaj




Dip Nb General Surgery Clinical Tutorials Dr T M Joseph 14



1
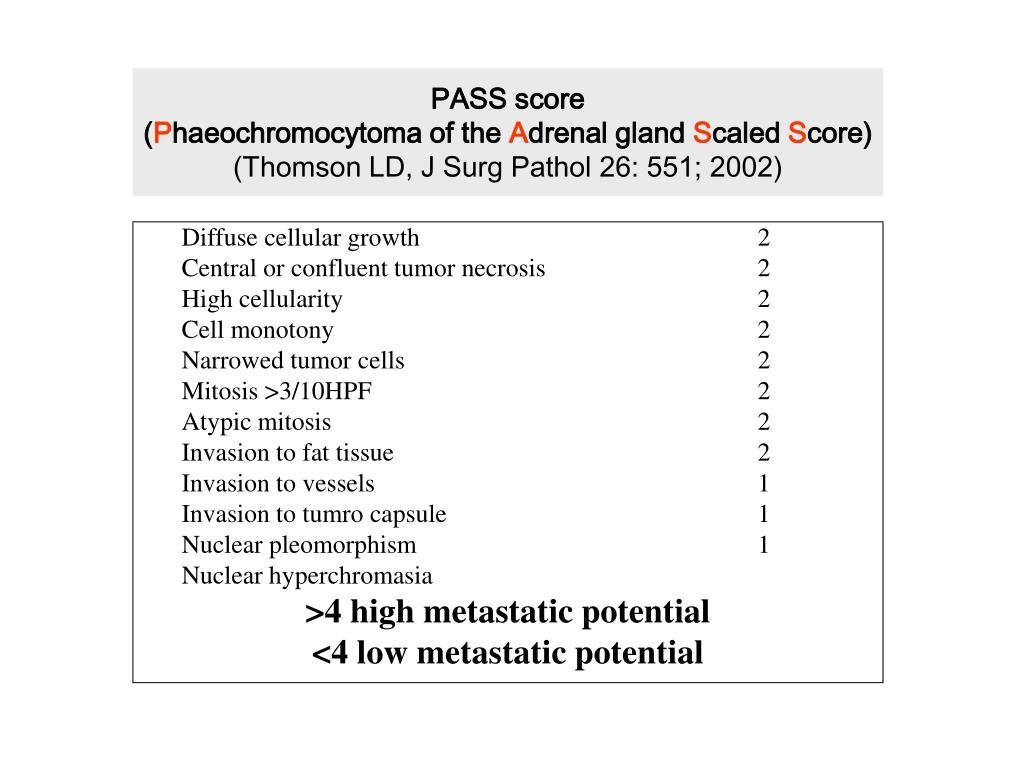



Ppt Pheochromocytoma Powerpoint Presentation Free Download Id




Binla Book



2




Edgar V Lerma Pheochromocytoma 5 Hs H Ypertension H Eadache H Yperhidrosis H Yperglycemia H Ypermetabolism Nephpearls Asnbrcu T Co Xcgcbcytr8




Southern Regional Meeting 17 New Orleans La February 11 13 17 Jim



Www E Kjp Org Pdf 10 Pn 31 4 236




Medical Mnemonics Pdf Txt



1



Pheochromocytoma Practice Essentials Pathophysiology Etiology
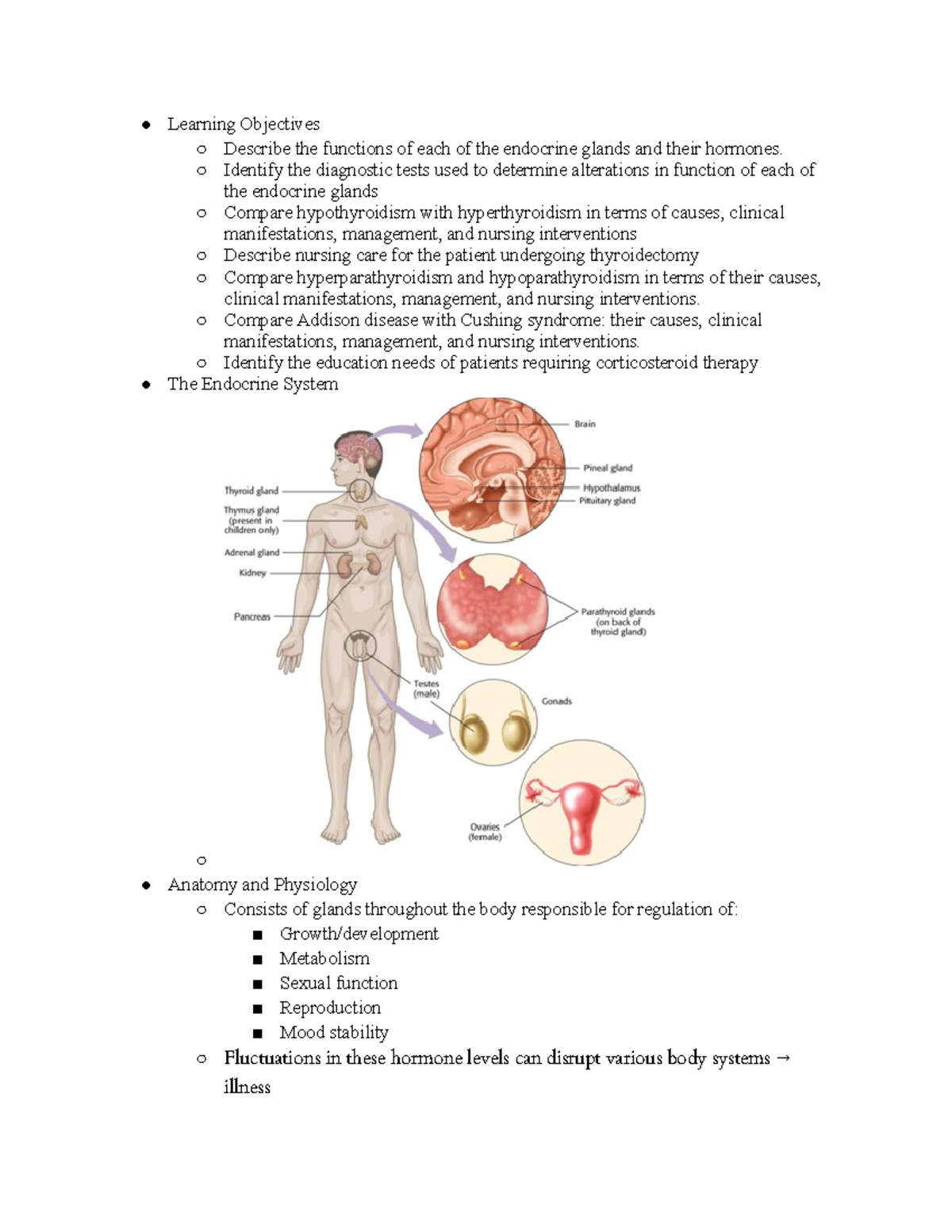



Care Of Pts With Endocrine Disorders Studocu




4zy7bwcxfhwowm



Pdf Decreased Succinate Dehydrogenase B In Human Hepatocellular Carcinoma Accelerates Tumor Malignancy By Inducing The Warburg Effect




History Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertension Ppt Video Online Download




History Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertension Ppt Video Online Download
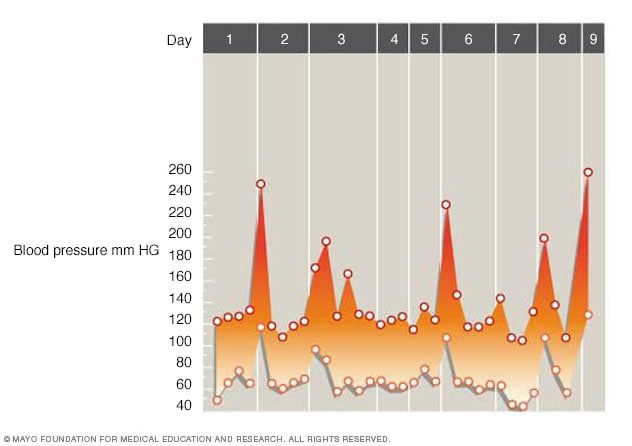



Pheochromocytoma Symptoms And Causes Mayo Clinic



Mysterious Inhibitory Cell Regulator Investigated And Found Likely To Be Secretogranin Ii Related Peerj



Www Epa Gov Sites Production Files 19 02 Documents Ambient Wqc 2378tetrachlorodibenzo 1984 Pdf




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders By Linda Self



Http Www Ingentaconnect Com Content Ben Ctmc 02 Art Crawler True




Pheochromocytoma




Pheochromocytoma Wikipedia



Www E Kjp Org Pdf 10 Pn 31 4 236



2



Http Www Ucsfcme Com 17 Mdm17p01 Slides 3 Final schedule one time print Mdm17p01 Pdf



Core Ac Uk Download Pdf Pdf




Assessment And Management Of Patients With Endocrine Disorders



Nerve Growth Factor Stimulates Interaction Of Cayman Ataxia Protein Bnip H Caytaxin With Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 In Differentiating Neurons




Adrenal Medulla Disorders Pheochromocytoma Medical Surgical Nursing Endocrine 1 8 15 Nurse Angie 18 Adrenal Medulla Disorders Pheochromocytoma A Course Hero



Genitourinary System




Pocket Medicine Sudirman Katu




Em Hyperkalemia And Endocrine Emergencies Flashcards Quizlet




Anesed




2 Nurse Critical Care Nursing Ideas Critical Care Nursing Nurse Nursing Students



Www Medicinebau Com Uploads 7 9 0 4 Recall 8th Pdf




Pheochromocytoma High Blood Pressure Headaches And Anxiety Headaches Anxiety Nervousness And Hypertension




Adrenal Medulla Disorders Pheochromocytoma Medical Surgical Nursing Endocrine 1 8 15 Nurse Angie 18 Adrenal Medulla Disorders Pheochromocytoma A Course Hero



2




Pocket Medicine Sabatine 7th Edition




Pheochromocytoma Wikipedia




Edgar V Lerma Pheochromocytoma 5 Hs H Ypertension H Eadache H Yperhidrosis H Yperglycemia H Ypermetabolism Nephpearls Asnbrcu T Co Xcgcbcytr8



Http Www Ingentaconnect Com Content Ben Ctmc 02 Art Crawler True




Headache In Pheochromocytoma Headache Hypertension




Pheochromocytoma
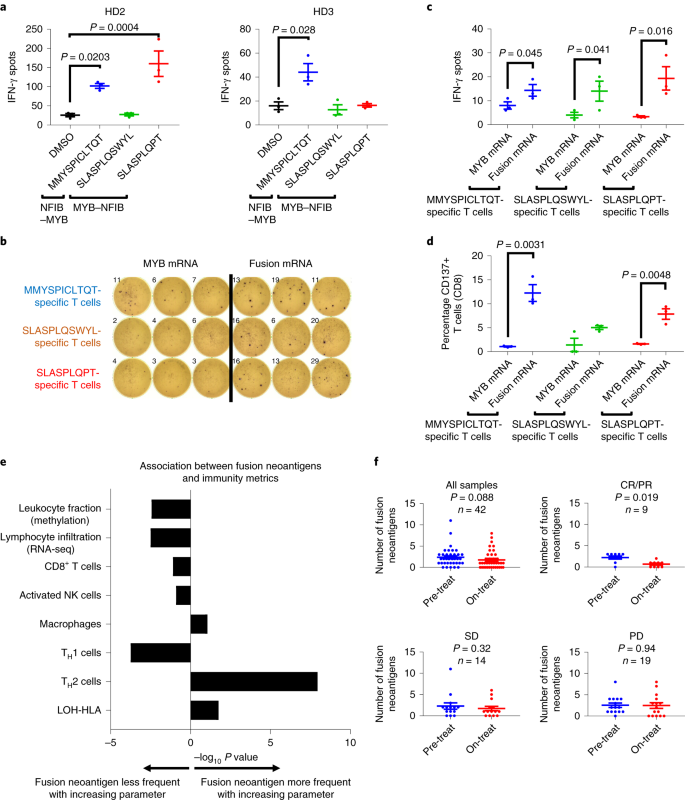



Immunogenic Neoantigens Derived From Gene Fusions Stimulate T Cell Responses Nature Medicine




Osmosis Many Health Professional Students Are In The Facebook




Insulin Is A Potential Antioxidant For Diabetes Associated Cognitive Decline Via Regulating Nrf2 Dependent Antioxidant Enzymes Sciencedirect




History Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertension Ppt Video Online Download



Q Tbn And9gcq53i2xt9hqrw3ulqxmuxjf3v1efy359etrqsfu4iiddkrxefx0 Usqp Cau




Pdf Pocket Medicine The Massachusetts General Hospital Handbook Of Internal Medicine Tai Hoang Nguyen Academia Edu
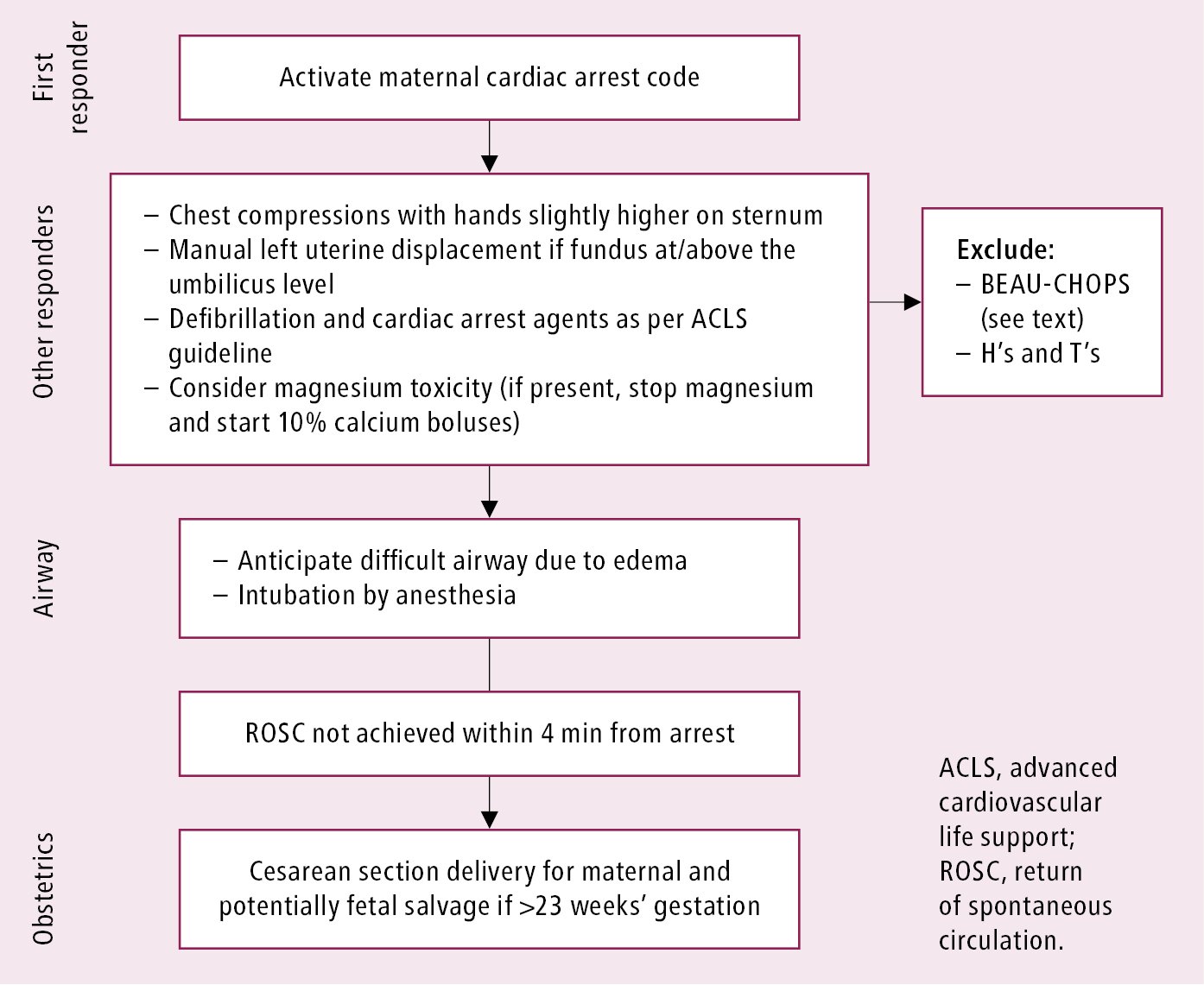



Amniotic Fluid Embolism Afe Pregnancy Related Conditions Diseases Mcmaster Textbook Of Internal Medicine



Antihypertensive Treatment For The Neurological Patient A Nursing Challenge Document Gale Academic Onefile




Pheochromocytoma




Cleveland Clinic Cardiovascular Emergencies Virtual Medical School




6 Teaching Nursing Assessment Pheochromocytosis 1462 1492 93 Pheochromocytoma Course Hero



Nerve Growth Factor Stimulates Interaction Of Cayman Ataxia Protein Bnip H Caytaxin With Peptidyl Prolyl Isomerase Pin1 In Differentiating Neurons




Applications Of Nmr Spectroscopy To Systems Biochemistry Abstract Europe Pmc



Ec Europa Eu Research Participants Documents Downloadpublic Documentids e5b56e9342 Appid Ppgms




Ppt History Signs And Symptoms Of Hypertension Powerpoint Presentation Id


コメント
コメントを投稿